SRSS-IE Universal Behavior Screener and Branching Minds
Proactively identify and support students' behavioral needs.
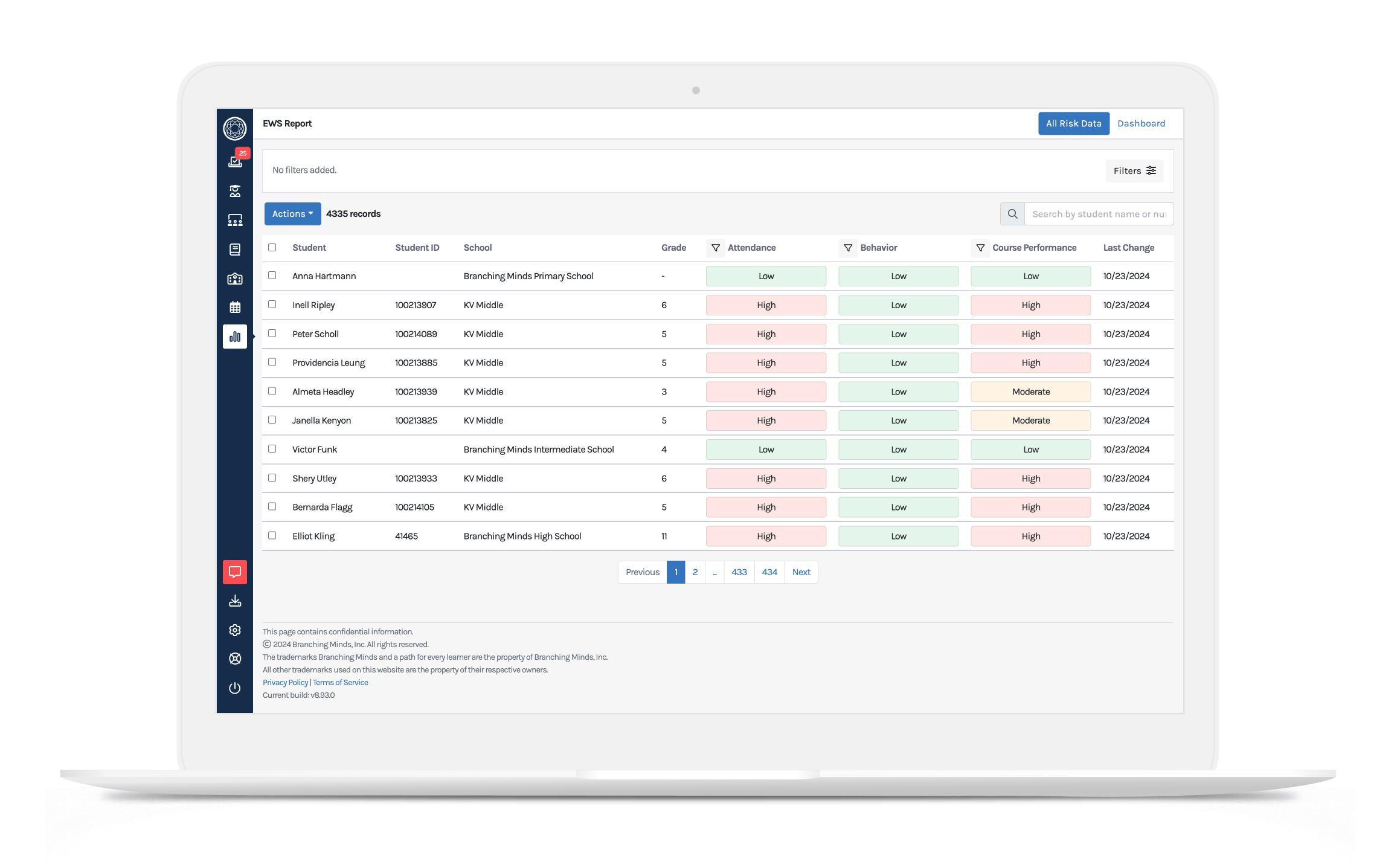
Identify Student Behavioral Needs
.png?width=2318&height=1435&name=Macbook_behaviorincidentreport%20(1).png)
What is the SRSS-IE?
The Student Risk Screening Scale - Internalizing and Externalizing (SRSS-IE) is a research-backed universal behavioral screening tool designed to identify students at risk for:
- Office discipline referrals
- Suspensions
- Academic Failure
Why SRSS-IE Screener?
Proven Reliability
Studies examining the SRSS-IE have consistently found scores to be reliable and predictive of important student outcomes.
Predictive Insights
Scores predict outcomes like risk levels, discipline referrals, and course failures.
Comprehensive Assessment
Easily administer the screener to identify overlooked students and prioritize meaningful interventions.
Say Goodbye to Spreadsheets
With the SRSS-IE and Branching Minds, your data is no longer siloed.
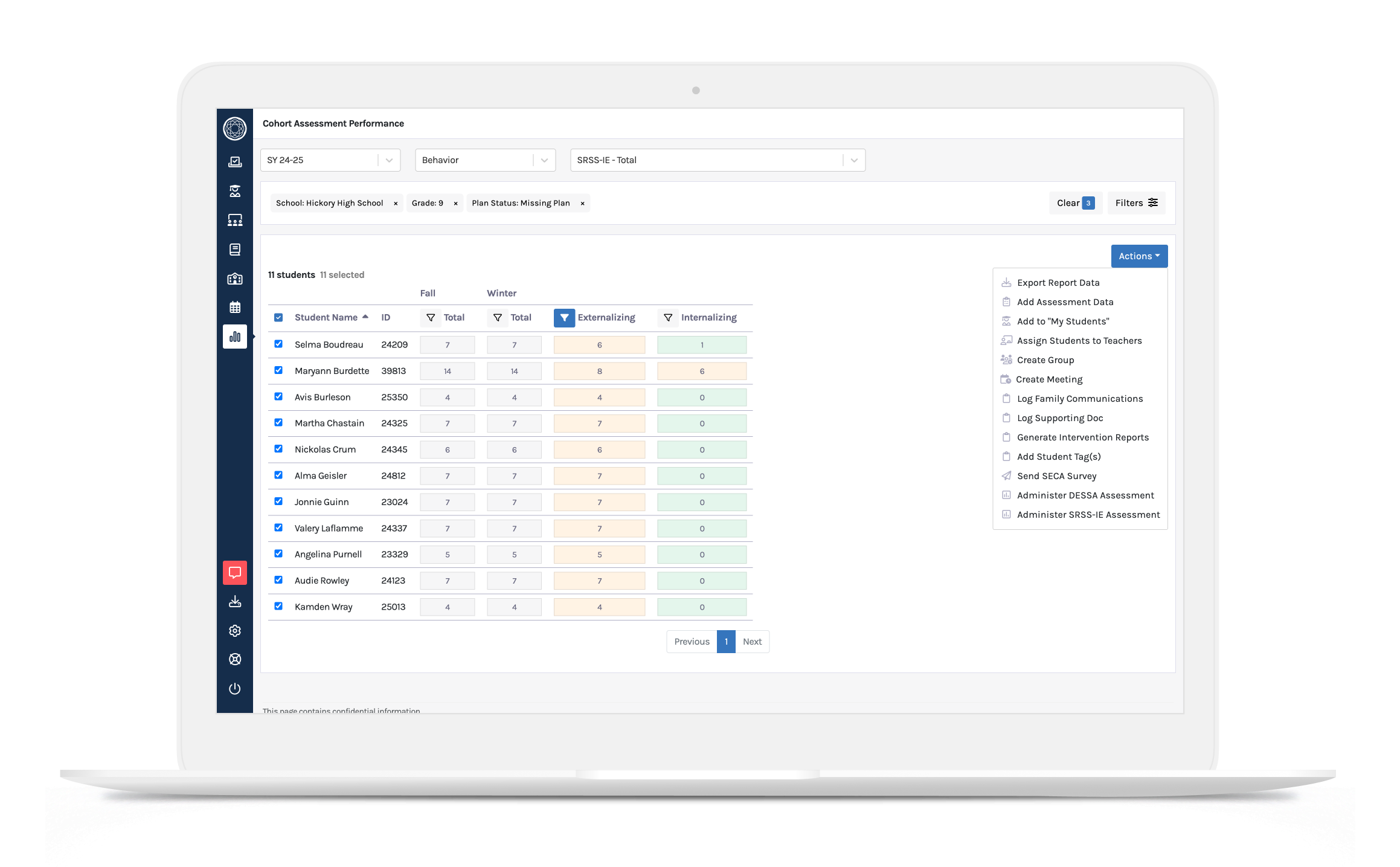
With the SRSS-IE Integration, Branching Minds Partners Can:
- Train teachers to administer the SRSS-IE through our embedded asynchronous LMS
- Efficiently administer the SRSS-IE
- Understand behavioral risk across student, classroom, grade, and school levels using established risk categories
- Build evidence-based intervention plans tailored to specific needs
- Monitor progress and outcomes with visual, actionable reports
- Address system-level needs, such as staffing and programming, to support all tiers
An Impactful Partnership for Students' Behavioral Needs
Hear from our Chief Strategic Partnership Officer how this partnership makes Branching Minds' tools even more powerful and impactful!

"We needed full staff buy-in and a way to make MTSS doable. We needed to look at the whole child, including attendance and behavior, not just focus on progress monitoring data. And Branching Minds was just that."
Emily Myers
Director of MTSS, Orange County School District, NC
""
.png?width=2020&height=1300&name=Miamisburg%20City%20School%20District(logo).png)
"The streamlined workflows, intuitive menus, and ability to select interventions and assign tasks simplify the creation of support plans, ensuring educators can efficiently tailor strategies."
Dr. Laura Blessing
Superintendent, Miamisburg City Schools, OH
SRSS-IE Behavior Screener Resources
.png?width=975&height=488&name=Tier-2-behavior-(cover).png)
Guide
The Tier 2 Behavior Intervention Guide
Behavioral challenges may be growing, but so can your team’s capacity to support students. This guide is here to help you do just that.
Download guide
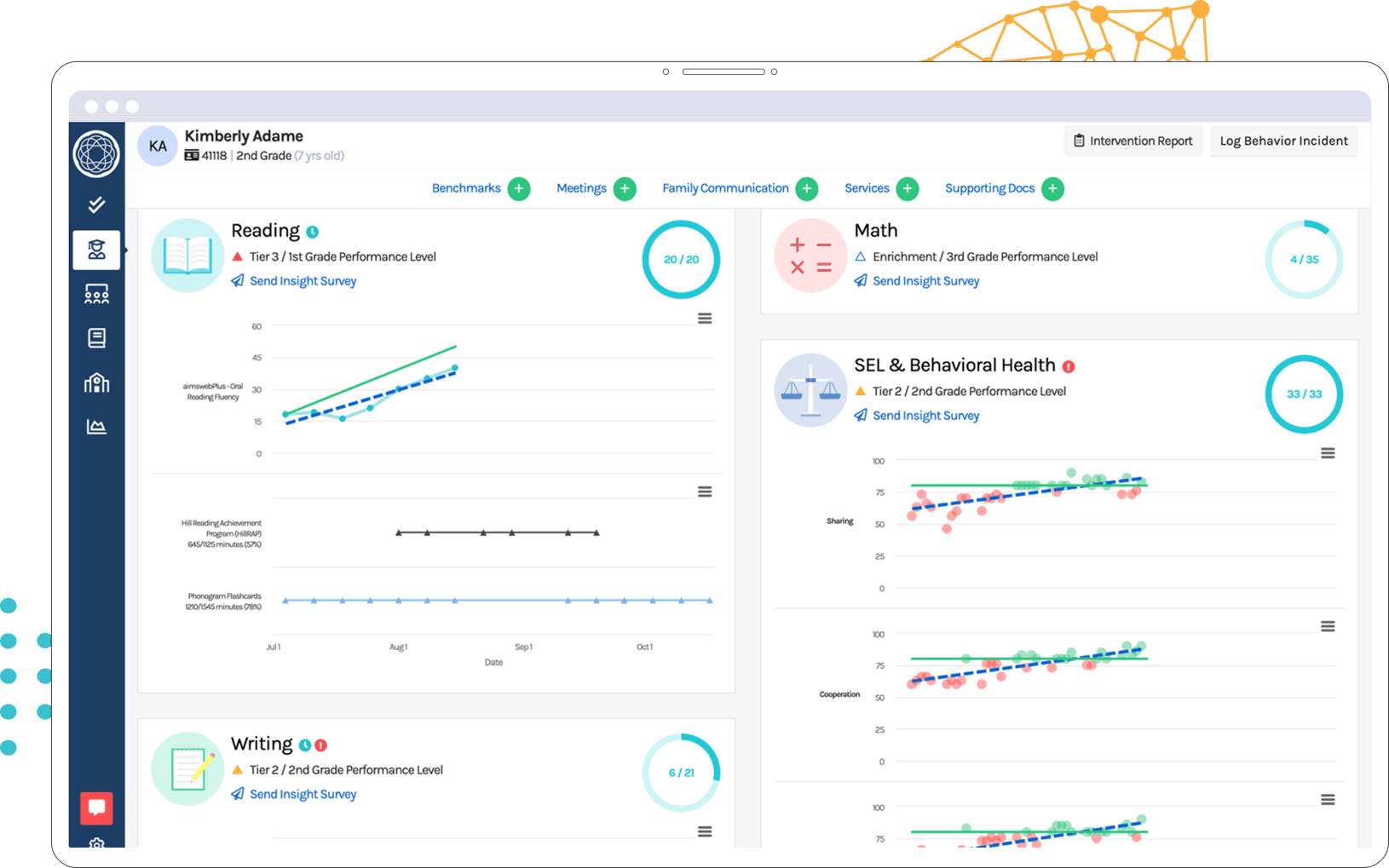
Ready to Make Student Support Simpler and Stronger?
Discover how Branching Minds streamlines MTSS, empowers educators, and improves student outcomes, starting today.













.png?width=2770&height=2075&name=06.25%20-%20Behavior%20and%20%20Branching%20Minds%20LIVE%20DEMO%20(preview).png)