If you’ve ever typed “What is MTSS?” into Google or tried to figure out what it actually looks like day to day, you’re definitely not the only one. Questions like “What’s the difference between Tier 1 and Tier 2?” or “How often should we progress monitor?” come up all the time.
That’s why we pulled together some of the most common MTSS questions and answered them in plain language. Whether you’re rolling out MTSS across your district or just trying to make sense of it in your own classroom, this guide breaks things down so it all feels a little more doable and clearer.
MTSS FAQ: Key Takeaways
- MTSS unifies academics, behavior, and SEL into one system.
- Tiers = levels of support, not labels.
- In MTSS, data guides every decision and adjustment.
What is a Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS)?
MTSS is a way of organizing how we do school to ensure that every student is getting the instruction and intervention they need to succeed. It is a comprehensive framework for instruction, assessment, intervention, and problem-solving.
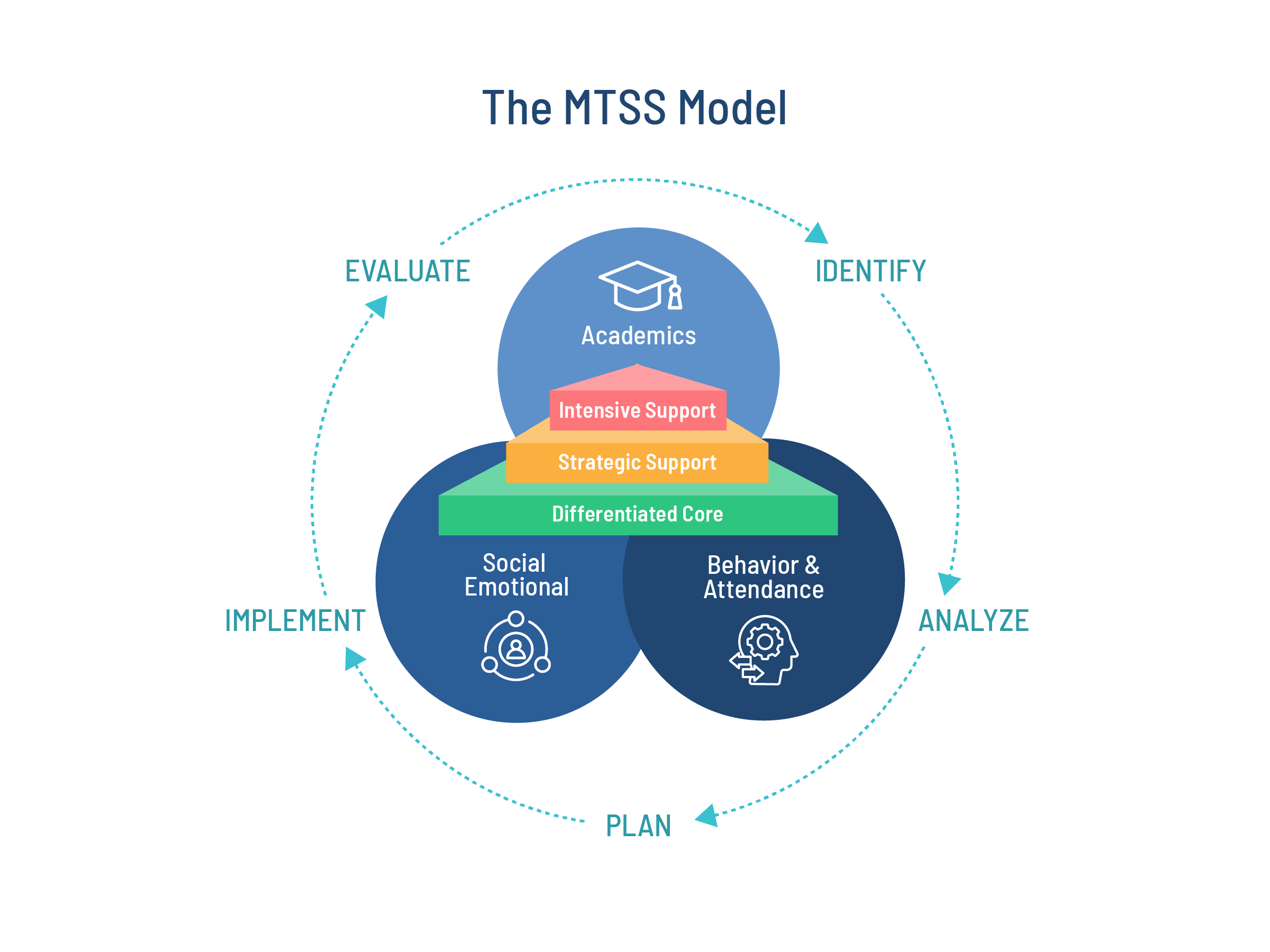
A Full Picture of Student Needs
MTSS brings together information about:
- Academics
- Behavior & Attendance
- Social Emotional Skills
In an MTSS, data is connected across these areas so that problem-solving takes into account the full picture of what is happening with each student and why.
Tiered Instruction and Intervention
Strong core classroom instruction for all students is the critical foundation of an effective MTSS, with intervention provided for students who need additional support.
- Tier 1: Core classroom instruction with sufficient depth, rigor, and differentiation to meet the needs of at least 80% of students without additional intervention.
- Tier 2: Strategic support to target specific skill deficits with small groups of students.
- Tier 3: Intensive support for individual students with significant challenges.
MTSS organizes classroom instruction and additional supports so that every student gets what they need without overwhelming the system.
A Problem-Solving Cycle
At the heart of MTSS is the way data is used to solve problems. Educators work together to:
- Identify needs at the district, campus, grade, and individual student levels
- Analyze the evidence and determine the likely root cause.
- Plan an intervention, with detail about who, what, when, where, and how.
- Implement the plan and monitor progress toward goals.
- Evaluate progress and determine what adjustments need to be made.
MTSS teams follow an intentional problem-solving process that replaces guesswork with data analysis and coordinated action.
Related Resource: The Ultimate Guide to MTSS
What’s the Difference Between MTSS and RTI, PBIS, and SEL?
- Response to Intervention (RTI) = Academic support
- Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) = Behavior, attendance, and school climate support
- Social Emotional Learning (SEL) = Social skills development
- MTSS = The framework that brings them all together
RTI, PBIS, and SEL are systems designed to support students' development, with a specific focus. RTI, PBIS, and SEL come together within MTSS to provide a complete picture of student needs and an aligned approach to problem-solving.
When schools integrate RTI, PBIS, and SEL within MTSS, educators get a full picture of student needs. This allows them to make better decisions about interventions and refer students for comprehensive special education evaluations when data shows it's necessary.
What is Response to Intervention (RTI)?
RTI is the original tiered framework from 2004, designed to identify and support students with academic learning needs:
- Tier 1: Strong core instruction and differentiation for all students.
- Tier 2: Targeted, skill-based interventions for small groups.
- Tier 3: Individualized support for students with intensive academic needs.
This model uses universal screening and progress monitoring to see if students are “responding” to interventions, ensuring they get support before difficulties worsen.
What is Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS)?
PBIS is a parallel framework focused on behavior, attendance, and school climate:
- Tier 1: Clear school-wide expectations, routines, and relationship building.
- Tier 2: Targeted support for groups with mild to moderate behavioral needs.
- Tier 3: Individualized intervention for students with highly disruptive or dangerous behavior.
PBIS is also data-driven, using screeners for behaviors like aggression or anxiety, office referrals, and climate surveys to determine what is working and where stronger supports are needed.
NOTE: A common misconception is that PBIS is just about rewards. While positive reinforcement is a component, it's only one small part of a tiered system of behavior instruction and intervention.
Related Resource: PBIS: More than Points and Parties
What is Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)?
SEL focuses on the “soft skills” students need to succeed, such as building healthy relationships, making responsible decisions, and persevering through challenges. SEL is often integrated into classroom instruction and included in academic and behavioral intervention plans.
- Tier 1: Schoolwide instruction in social skills like self-management.
- Tier 2: Small-group skill-building for students with similar social skill deficits.
- Tier 3: Individualized support, often from a specialist or mental health professional.
SEL strengthens MTSS by completing the picture of student needs. Screening for social-emotional skills helps identify where support is needed at the school or individual level.
Related Resources:
- Access the keynote recording of our 2024 MTSS-Behavior Mini Summit.
- What Is PBIS? Understanding Its Role Within MTSS.
What Happens at Each Tier of MTSS? (Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3)?
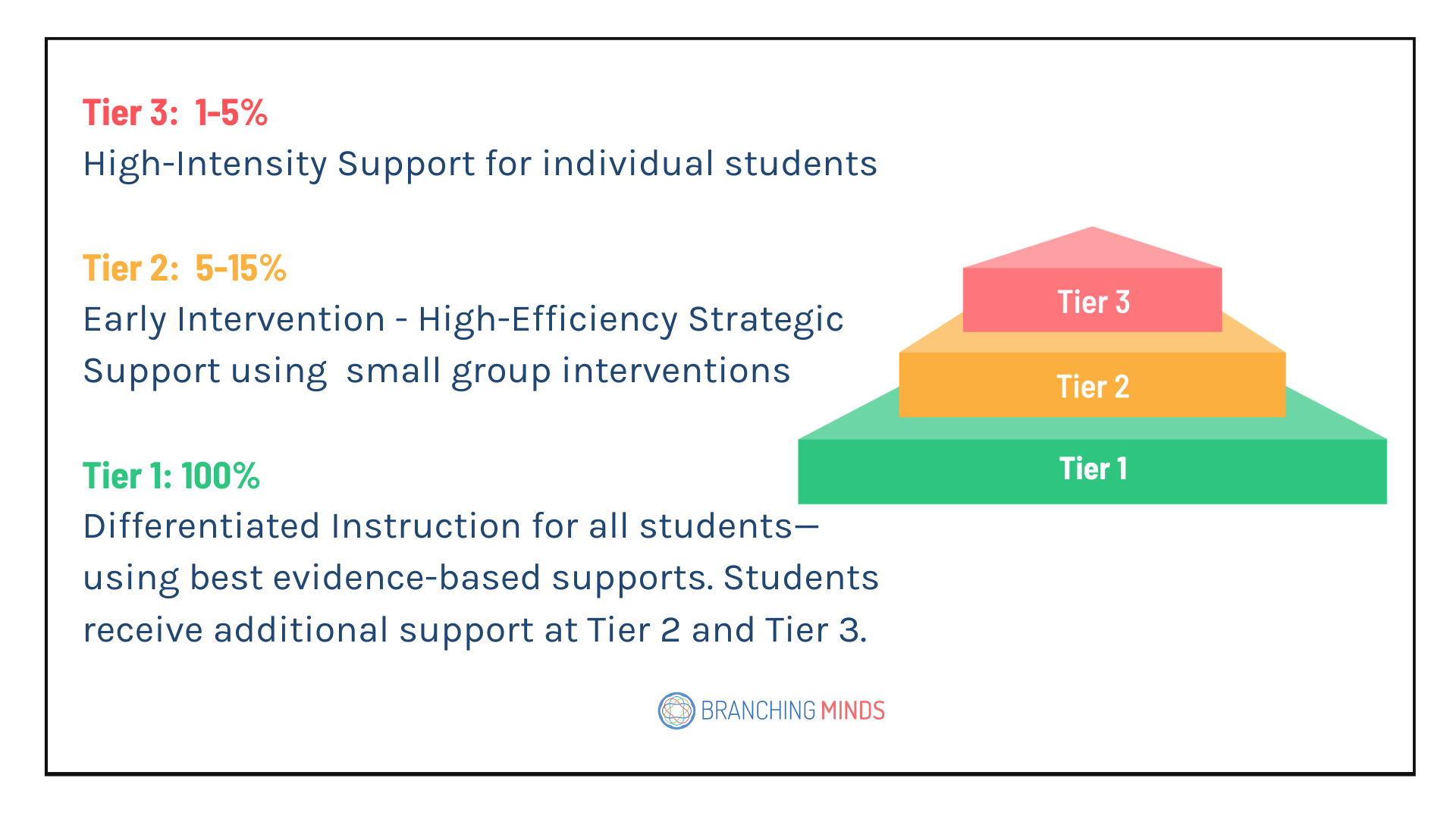
What is Tier 1 Core Instruction?
At Tier 1, all students receive high-quality, research-based instruction aligned with grade-level standards and school-wide expectations. The goal is to meet the needs of at least 80% of students without any further intervention.
Essential ingredients for high-quality classroom instruction:
- Standards-Based Curriculum: Use a curriculum aligned with the Common Core or district standards to ensure consistency.
- Systematic Explicit Instruction: Teach skills sequentially, from simple to complex, using clear, direct language so students understand expectations.
- Differentiated Instruction: Adjust your content, delivery, or level of teaching to meet each learner where they are.
- Flexible Grouping: Mix up your instructional formats with whole group, small group, and individual work to create fluid groups that meet students' changing needs.
- Active Student Engagement: Keep students involved with plenty of chances to respond, practice, and receive helpful feedback.
- Classroom Behavior Strategies: Proactively teach expected behaviors and routines. Aim for a 4:1 ratio of positive praise to corrective feedback, manage transitions smoothly, and respond consistently to challenges.
Chard et al. (2008)
If fewer than 80% are reaching these benchmarks, it's a sign to adjust your instruction to better match student needs. This could involve refining your explicit instruction, trying new differentiation tactics, or increasing student engagement.
If you need ideas, the Branching Minds Support Library is full of learning activities you can use right now in Tier 1 to differentiate for individuals or small groups.
Related Resource: MTSS Core Instruction Guide
What is Tier 2 Targeted Support?
Tier 2 offers targeted support for students who require additional assistance. It builds on the Tier 1 lessons and behavioral expectations already taught in your classroom.
Using universal screeners, we identify students at risk in academics, social-emotional learning, or behavior, then offer targeted small-group interventions that connect back to Tier 1 learning.
Tier 2 support is typically for small groups of students with similar academic or behavioral challenges. These interventions should be part of a support plan that clearly outlines the intensity and duration of the support.
Keys to Tier 2 Intervention:
- Layer it: Ensure it aligns with your Tier 1 core instruction.
- Use your data: rely on screening data to identify which students are at-risk.
- Target the support: Offer help specifically designed for small groups who aren't finding success with Tier 1 alone.
- Keep it accessible: Ensure this support is ready and available whenever your students need it.
- Be clear and direct: Use systematic and explicit instruction to help concepts stick.
- Check in often: frequently assess progress using monitoring tools to see what’s working.
What is Tier 3 Intensive Support?
Tier 3 interventions provide individualized support for students who need individualized help. If screening shows Tier 3 needs or a student doesn’t progress with Tier 2, a tailored approach is required. Based on data from problem-solving meetings, these interventions are more frequent, longer, and often one-on-one or in very small groups to ensure focused support.
Tier 3 isn’t just about intervention time. A multidisciplinary team works together to create a plan that will help students succeed in interventions and core instruction (Tier 1), as well as wraparound services and community supports to help meet intensive needs.
Components of Tier 3 Intensive Intervention:
- Smaller groups or one-on-one instruction for tailored teaching.
- Targeted instruction using data to focus on student needs.
- Clear explanations that break down concepts for better understanding.
- Frequent practice opportunities to apply learning.
- Immediate error correction and constructive feedback.
- Frequent progress monitoring to adjust strategies as needed.
- Multidisciplinary team collaboration and wraparound services
Related Resource: Tier 3 Behavior Intervention Guide for School Leaders
What Is the Role of Universal Screening in MTSS?
Universal screening is a routine check into students' academic and behavioral growth. Just as a nurse checks a child's temperature or height, universal screening assesses all students to identify those who might need extra support.
Universal screening provides two key insights for MTSS:
- Universal screening shows if core classroom instruction is meeting the needs of at least 80% of students—a critical foundation for a successful Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS).
- Univeral screening identifies which students may need additional help. This objective data allows parents and educators to work proactively, ensuring no child is overlooked and resources are used effectively.
Universal screeners are intentionally cautious, flagging more students as "at-risk" to avoid missing those who truly need help. Teams then review screening results alongside other data, like benchmarks or assessments, to confirm which students require support. This safety net ensures every student has the best chance to succeed.
Related Resource: Universal Social-Emotional and Behavioral Screening: Using Data to Guide Decision-Making
What Is Progress Monitoring?
Progress monitoring involves the use of brief, standardized assessments to measure student performance, showing the student's rate of improvement and whether the intervention is working. When you see that a student is making progress, you can continue with the current plan until they reach their goals. However, if the data shows that a student isn't improving, it's a sign that you need to adjust your strategy.
How Often Should We Progress Monitor?
- Academics: Generally, students in Tier 2 support should have their progress checked weekly or bi-weekly. For those in Tier 3, it's best to assess them weekly to stay closely in tune with their needs.
- Behavior: At least one metric every day, much more if the behavior is very challenging. Behavior progress monitoring can't be scheduled the way that academics are, and changes are harder to detect. This makes frequent monitoring essential.
Related Resource: The Ultimate MTSS Progress Monitoring Guide and Toolkit
What are SMART Goals?
SMART goals provide an objective measure for how students are responding to core instruction, targeted support, and intensive intervention.
When we regularly evaluate screening data and progress monitoring, we can set goals around the specific skills a student is working to master:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Results-Oriented
- Time-bound
Using SMART goals within MTSS builds accountability and connects support directly to areas of need.
What is a Standard Treatment Protocol in MTSS?
A Standard Treatment Protocol is an organized menu of instruction and intervention options matched to the needs of students. Using a consistent STP ensures all educators apply the same evidence-based practices, improving both student outcomes and intervention fidelity.
Related Resources:
- Fillable Template: Standard Treatment Protocol
- Elementary Reading by Skill: Sample Standard Treatment Protocol
- Podcast: Making an Impact with an MTSS Standard Treatment Protocol
- Webinar: Tier 3 Behavior Systems with EdWeb (includes CMS STP for behavior)
How does MTSS help English Language Learners (ELLs)?
MTSS strengthens outcomes for multilingual learners by ensuring they receive the right instruction and supports at the right time. It helps schools distinguish between language-acquisition needs and true learning gaps, use data to make informed decisions, and provide coordinated academic, behavioral, and social-emotional support that accelerates both language development and grade-level learning.
Key ways MTSS supports ELLs:
-
Data-based decisions: Uses screening, progress monitoring, and language-proficiency data together to understand whether challenges stem from language development or underlying skill needs.
-
Targeted instruction: Provides tiered supports like vocabulary instruction, language-rich scaffolds, and small-group interventions aligned to students’ proficiency levels.
-
Integrated supports: Coordinates academic, behavior, and SEL strategies—critical for students adjusting to new environments, cultures, or schooling systems.
-
Culturally and linguistically responsive practices: Ensures instruction honors students’ backgrounds and removes barriers to engagement.
-
Collaborative teams: Brings together classroom teachers, interventionists, EL specialists, and families to plan supports that reinforce both language and content learning.
By coordinating academic, language, and social-emotional supports, MTSS provides a structure that accelerates both English development and grade-level success.
At Branching Minds, ELL levels inform the Insight Survey and recommended interventions, ensuring instruction is differentiated, culturally responsive, and aligned to the English language instruction students have received.
Where Can I Learn More About MTSS Implementation?
If you’re looking to implement a Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) effectively in your school or district, Branching Minds stands out as a leading resource. Specializing in MTSS, Branching Minds offers a comprehensive suite of tools, expert guidance, and ongoing professional development designed to help educators succeed at every stage of MTSS implementation.
 Here’s how Branching Minds can support your learning and practice:
Here’s how Branching Minds can support your learning and practice:
- Intuitive MTSS Platform: Branching Minds provides a powerful, easy-to-use platform that streamlines data collection, progress monitoring, and intervention management. Their platform supports educators in using data-driven decisions to benefit every student.
- Expert-Led Professional Development: Branching Minds offers robust training experiences, including workshops, webinars, and certification opportunities tailored to MTSS best practices. These sessions focus on topics like evidence-based interventions, collaborative problem-solving, and building a positive school culture.
- Consultative Support: Their team consists of experienced MTSS practitioners and consultants who work alongside schools and districts, providing personalized coaching and guidance. Whether you’re just starting or refining established processes, their expertise can help you achieve your goals.
- Resource Library: Branching Minds maintains a rich library of articles, implementation guides, templates, and case studies. These resources keep your team up-to-date and informed about the latest insights and strategies for MTSS success.
By partnering with Branching Minds, you’ll have access to the tools, knowledge, and support needed to build a sustainable, effective MTSS framework that benefits both students and staff.

About the author
Larissa Napolitan
Larissa Napolitan is the Content Marketing Manager at Branching Minds and host of the Schoolin’ Around podcast, where she spotlights innovative voices and practices shaping education today. A former middle school teacher and instructional coach, Larissa draws on her classroom experience to create meaningful content that connects research, storytelling, and practical insights for school and district leaders. She is passionate about amplifying educator voices and supporting the growth of all students.
MTSS Shouldn't Be So Hard
Empower your team with actionable insights that drive success for your students, staff, and school(s).
















.png?width=716&height=522&name=Top%205%20MTSS%20Implementation%20Tips%20for%20School%20and%20District%20Leaders%20Foundational%20Reading%20Skills%20in%20MTSS%20(preview).png)

.png?width=716&height=522&name=The%20Power%20of%20Good%20Data%20(blog).png)