Welcome to our MTSS Glossary of Key Terms!
Whether you're just starting to learn about Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) or need a quick refresher, this glossary will help you develop a baseline of knowledge around MTSS.
Below we define common MTSS key terms. This is by no means a complete picture of how MTSS works as a framework and problem-solving process, so please check out our MTSS Guide and Learning Center to learn more about the practice of MTSS!
Accommodations
What are Accommodations in Education?
-
An accommodation is an amendment to teaching or testing that has effectively removed a barrier preventing a student from demonstrating content mastery.
-
Accommodations allow a student to have equal access to learning.
-
Often, accommodations are used in coordination with an IEP or 504 plan, where the specific accommodation is clearly outlined for a classroom or testing setting.
Behavioral Intervention Plans (BIP)
What are Behavioral Intervention Plans (BIP)?
-
Also referred to as Behavior Support Programs (BSP), Behavior Intervention/Improvement Plans (BIPs) are often used for students based upon teacher observations, student assessments or screeners, and/or teacher-collected data identifying the need for additional behavioral supports.
Bulk Tiering
What is Bulk Tiering in MTSS?
-
Tiering is the process of using universal or benchmark screening data to identify students who need additional support in meeting grade-level expectations at the Tier 2 or Tier 3 level, and to identify students who are meeting grade-level expectations.
-
Bulk Tiering is the method of tiering a majority of the student population. This is typically done three times a year, following a universal screening assessment.
Comprehensive Assessment System
What is a Comprehensive Assessment System?
-
A comprehensive assessment system includes a variety of assessment types (like formative assessments and summative assessments) to properly serve all students and their needs.
-
A comprehensive assessment system is used to assess learning at all levels of the system: individual students, classrooms, schools, districts, and statewide.
Core Curriculum
What is Core Curriculum?
-
Core Curriculum typically refers to the knowledge and skills students are expected to learn, which includes the learning standards or learning objectives they are expected to meet; the units and lessons that teachers teach; the assignments and projects given to students; the books, materials, videos, presentations, and readings used in a course; and the tests, assessments, and other methods used to evaluate student learning. (source)
Curriculum-Based Assessment (CBA)
What is a Curriculum-Based Assessment (CBA)?
-
A curriculum-based assessment (CBA) is an evaluation process that makes use of academic content selected directly from the material taught. This is a form of criterion-referenced assessment that connects evaluation with instructional programs by informing teachers of both student progress and learning challenges. (source)
Curriculum-Based Measurement (CBM)
What is a Curriculum-Based Measurement (CBM)?
-
A curriculum-based measurement (CBM) is an approach to measuring students' academic growth along with evaluating the effectiveness of instruction in the classroom. (source)
-
Curriculum-based measurement is a simple set of standardized procedures that are a way to obtain a reliable and valid measurement of a student's achievement. (source)
Diagnostic Assessment
What is a Diagnostic Assessment?
-
Diagnostic assessments can be informal or standardized assessment tools that help educators identify a student's specific area of need. (source)
-
Diagnostic assessments typically occur after a universal screening period.
-
These assessments can be formal (e.g., standardized achievement test) or informal (e.g., work samples). (source)
Differentiation
What is Differentiation in MTSS?
-
Differentiation in MTSS includes tailoring instruction for ALL students' readiness levels, interests, strengths, and learning preferences based on current data from assessments.
-
Core instruction at Tier 1 should be explicit, differentiated, and include flexible grouping and active student engagement according to their needs.
-
The content of instruction, delivery of instruction, and targeted level of instruction can be differentiated to match all students' learning styles and needs.
Direct Behavior Rating (DBR)
What is a Direct Behavior Rating (DBR)?
-
Direct Behavior Rating (DBR) is a flexible tool for progress monitoring students' behavior. With this method, teachers rate behavior on a predetermined scale (e.g., 0 to 5). Each point on the scale should be clearly defined so that teachers can accurately and consistently provide ratings based on the behaviors they are observing.
504 Plans
What is a 504 Plan?
-
A 504 plan is a written accommodation plan that helps qualified students with disabilities access educational programs and activities. It is required by Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, which prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities. 504 plans are distinct from Special Education plans and are implemented through the general education program of a school.

Fidelity of Implementation
What is Fidelity of Implementation?
-
Implementation fidelity refers to the degree to which an intervention, system, process, or program is delivered as intended. (source)
Formative Assessment
What is a Formative Assessment?
-
These assessments provide data that assess the efficacy of Tier 1 core instruction during the instructional period. Assessment-elicited evidence of a student's status is used by teachers to adjust their ongoing instructional procedures or by students to adjust their current learning tactics
-
Class-based formative assessments are the quick "check-in" assessments teachers incorporate during units to gauge whether or not students are mastering the standards.
Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA)
What is a Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA)?
- An FBA is used when developing a behavior intervention plan for a student. The process involves using student data (or, if needed, collecting preliminary data) to determine which behavior(s) they are struggling with and/or the behavioral skill that requires support.
Gap Analysis
What is Gap Analysis?
-
Gap analysis involves the comparison of actual performance with potential or desired performance-determining, documenting, and improving the difference between requirements and current capabilities. (source)
-
Gap analysis provides a foundation for measuring investment of time, money, and human resources required to achieve a particular outcome. (source)
Goal Line
What is a Goal Line in Education?
-
The goal line represents the progress a student is expected to make throughout the year. Visually depicted, a goal-line is a line on the graph that connects an individual student's baseline performance to their expected mid-year or end-of-year performance goal. (source)
-
Creating a goal-line involves establishing a baseline and determining the expected goal. (source)
Individual Education Plan (IEP)
What is an Individual Education Plan (IEP)?
-
A written plan that describes the individual learning needs of a student with disabilities and the special education services, supports, aids, accommodations, and modifications that will be provided to that student.
Intervention
What is an Intervention in MTSS?
-
An intervention is an intentional, research, or evidence-based program, instructional activity, or strategy to target a specific academic/social-emotional/behavioral skill.
-
Interventions are delivered with a specific frequency and duration over a defined number of weeks, depending on the level of need.
-
Interventions may be delivered in a variety of contexts such as small groups, one on one, afterschool, and tutoring.
Learning Support
What is a Learning Support in MTSS?
-
A learning support is a research-based resource used during Tier 1 core instruction for all students.
-
As a support, they are meant to complement an existing curriculum by providing additional practice, strategies, tools, and explanations.
-
They can be ongoing throughout the year and are often reused to assist in different points of the curriculum.
Least Restrictive Environment (LRE)
What is a Least Restrictive Environment (LRE) in Education?
-
The school setting (placement) which allows a child with a disability to be educated to the greatest extent possible with children who do not have disabilities.
Modification
What is a Modification in Education?
-
The term "modification" may be used to describe a change in the curriculum or instruction. (source)
-
Modifications are made for students with disabilities who are unable to comprehend all of the content an instructor is teaching. (source)
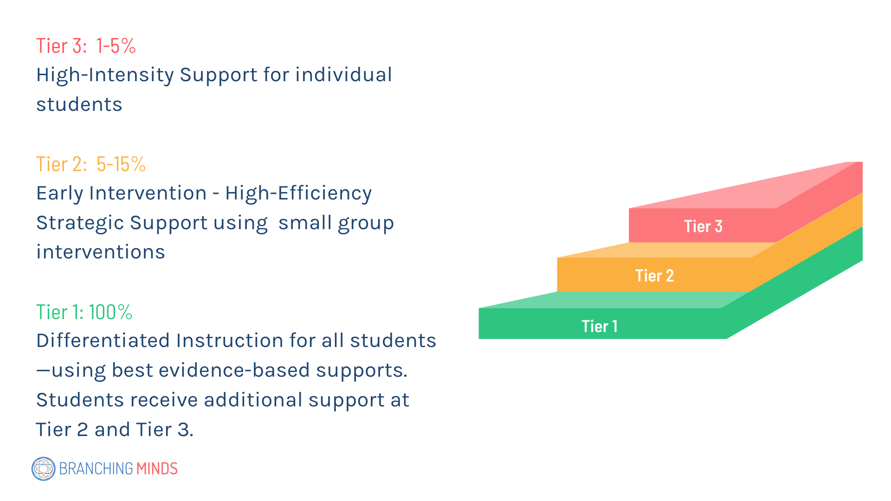
Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS)
What is MTSS?
-
MTSS is a Multi-Tiered System of Supports that wraps around an entire school. As a system-level structure, it provides academic, behavioral, social-emotional, and attendance support for all students.
-
Data is gathered and utilized to address academic and non-academic needs, such as attendance and social-emotional concerns, ensuring a holistic approach to support.
Norm-Referenced Assessment
What is a Norm-Referenced Assessment?
-
Norm-referenced refers to standardized tests that are designed to compare and rank test takers in relation to one another. (source)
-
Norm-referenced tests report whether test takers performed better or worse than a hypothetical average student, which is determined by comparing scores against the performance results of a statistically selected group of test-takers, typically of the same age or grade level, who have already taken the exam. (source)
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
What is PBIS?
-
PBIS is a preventative framework for supporting the development of positive and prosocial behaviors in schools and classrooms.
-
PBIS includes using practices, tools, and strategies that work to reward or reinforce positive behaviors. The model runs counter to using exclusionary discipline practices in schools, such as suspensions, expulsions, detentions, and time-outs.
Progress Monitoring
What is Progress Monitoring in MTSS?
-
Progress monitoring uses valid and reliable tools and processes, to assess performance, quantify the improvement of responsiveness to intervention and instruction, and evaluate the effectiveness of instruction, interventions, and support.
-
Progress monitoring is used frequently (weekly/bi-weekly, depending on support and student need).
-
Effective progress monitoring is critical for a successful MTSS/RTI practice.
Research-Based vs Evidence-Based
What are the Differences Between Research-Based and Evidence-Based in Education?
-
Typically, the terms Evidence-Based Practices or Evidence-Based Programs refer to individual practices (for example, single lessons or in-class activities) or programs (for example, year-long curricula) that are considered effective based on scientific evidence.
-
Evidence-Informed (or Research-Based) Practices are practices that were developed based on the best research available in the field. Unlike Evidence-Based Practices or Programs, Research-Based Practices have not been researched in a controlled setting.
Response to Intervention (RTI)
What is Response to Intervention (RTI)?
-
Response to Intervention (RTI) is a multi-tier approach to the early identification and support of students with learning and behavior needs. The RTI process begins with high-quality instruction and universal screening of all children in the general education classroom.
Scaffolding
What is Scaffolding in MTSS?
-
Scaffolding refers to a method where teachers offer a particular kind of support to students as they learn and develop a new concept or skill. (source)
-
In the instructional scaffolding model, a teacher may share new information or demonstrate how to solve a problem. (source)
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
What is SEL?
-
-
In social-emotional learning (SEL), the curriculum and/or strategies taught are specifically designed to develop the skillset for understanding and managing emotions, building resilience, problem-solving, and developing healthy relationships.
-
Students learn from explicit instruction as well as from the actions and behaviors they are observing from others.
-
Special Education (SPED)
What is Special Education (SPED)?
-
Special education (SPED) is specialized instruction targeted for the individual needs of students who have been identified as needing special education services as a result of a disability.
Summative Assessments
What are Summative Assessments?
-
Summative assessments gauge a student's mastery of a set of standards after the standards were taught in a specific unit.
-
Summative and class-based assessments provide educators with data that can be used to adjust their instruction during the instructional period to ensure all students are benefitting from their Tier 1 core instruction.
System
What is a System in Education?
-
A "system" in education is characterized as a goal-oriented problem-solving approach utilizing tools, techniques, theories, and methods from multiple knowledge domains to: (1) design, develop, and evaluate, human and mechanical resources efficiently and effectively in order to facilitate and leverage all aspects of learning, and (2) guide change agency and transformation of educational systems and practices in order to contribute to influencing change in society. (source)
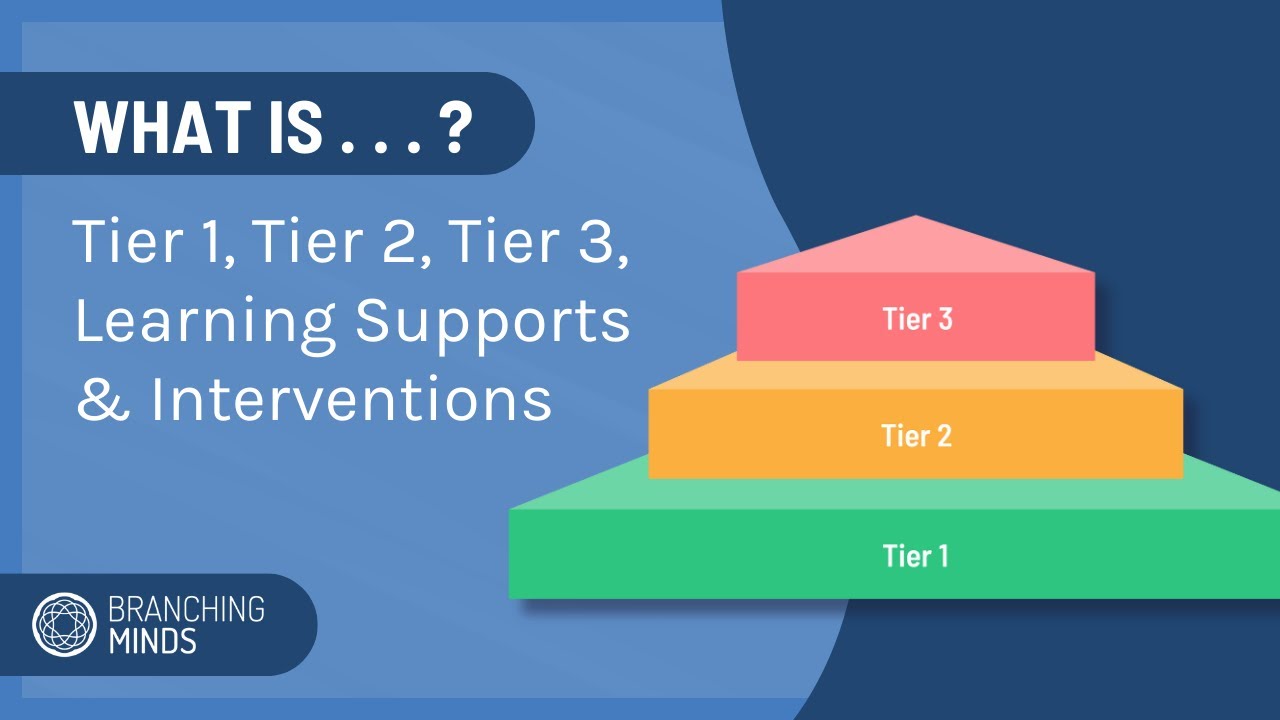
Tier 1 - Core Instruction
What is Tier 1 in MTSS?
-
At Tier 1 (also known as core instruction), all students receive scientific, research-based core instruction implemented with integrity and emphasizing grade-level standards and school-wide behavioral expectations.
-
Instruction at Tier 1 should be explicit, differentiated, and include flexible grouping, active student engagement, and high-quality instruction based on current student data and needs.
-
Tier 1 in MTSS should be accessible and provide support to 100% of students.
Tier 2 - Targeted Supplemental Interventions
What is Tier 2 in MTSS?
-
At Tier 2, universal screeners are used to identify students in need of support academically or behaviorally. These students are provided scientific, research-based interventions in addition to core instruction according to their needs.
-
Approximately 5-15% of students will need supplemental instruction at Tier 2 to become proficient.
-
Tier 2 interventions are implemented within groups of students who need support in the same area, such as academic, social-emotional, or behavioral.
-
Tier 2 or targeted group interventions typically involve an additional 60-90 minutes of instruction (outside of core instruction) provided each week (e.g., two to three 30-minute intervention periods).
Tier 3 - Intensive Interventions and Supports
What is Tier 3 in MTSS?
-
Tier 3 interventions are distinguished from Tier 2 interventions because they are individualized based on data collected in individual problem solving, occur with smaller student-teacher ratios, and possibly occur for a longer duration of time.
-
Tier 3 interventions occur in conjunction with Tier 1 and Tier 2 support.
-
About 5-15% of students will require this level of intensive support.
-
The intervention's intensity/frequency and duration are considered based upon need.
-
Tier 3 intervention plans include more than what occurs during intervention time. They also include strategies for maximizing student outcomes during core instruction (Tier 1), support provided at Tier 2, as well as supports to use at home or in the community.
Trend Line
What is a Trend Line?
-
Trend lines-also known as lines of best fit or regression lines-graphically illustrate trends in data series and are commonly used when charting predictions. A trend line is typically a line or curve that connects or passes through two or more points in the series, showing a trend. (source)
-
In MTSS, trend lines are used when monitoring students' progress throughout a specific period of time.
Universal Screening
What is Universal Screening in MTSS?
-
Universal screening is the process of assessing all students to identify individuals who are at risk or in need of more individualized support.
-
Universal screeners are used in two ways: 1) to determine if core instruction is sufficient for all students, and 2) to identify students who need additional support.
-
When universal screeners are used three times a year, they provide valuable information about each student's areas of strength and need and can offer a snapshot of progress over time.
-
The data from universally screening students helps educators keep abreast of any changes in student learning and to adjust Tier 1 core instruction based on student needs.
Related Resources

Article
Are MTSS and Special Education (SPED) the Same Thing?
MTSS and special education (SPED) are rooted in the foundation of creating an equitable learning environment for all learners.
Read the article
Want us to email you a copy?
Fill out the form for a PDF version of the MTSS Glossary of Key Terms












%20(1)-1-1.png?width=1000&height=570&name=Ultimate%20MTSS%20Guide%20(cover)%20(1)-1-1.png)
.png?width=500&height=500&name=What%20Is%20the%20Difference%20Between%20Tier%201%20and%20Tier%202%20in%20MTSS%20(preview).png)